Blog
What Is Pump Fan On Motherboard – A Complete Overview!

The pump fan header on a motherboard powers and controls the liquid cooling pump, ensuring efficient cooling and optimal system performance.
In this article, we’ll explore what a pump fan is, its role in your PC’s cooling system, and how to use it effectively.
Understanding the Pump Fan Header:
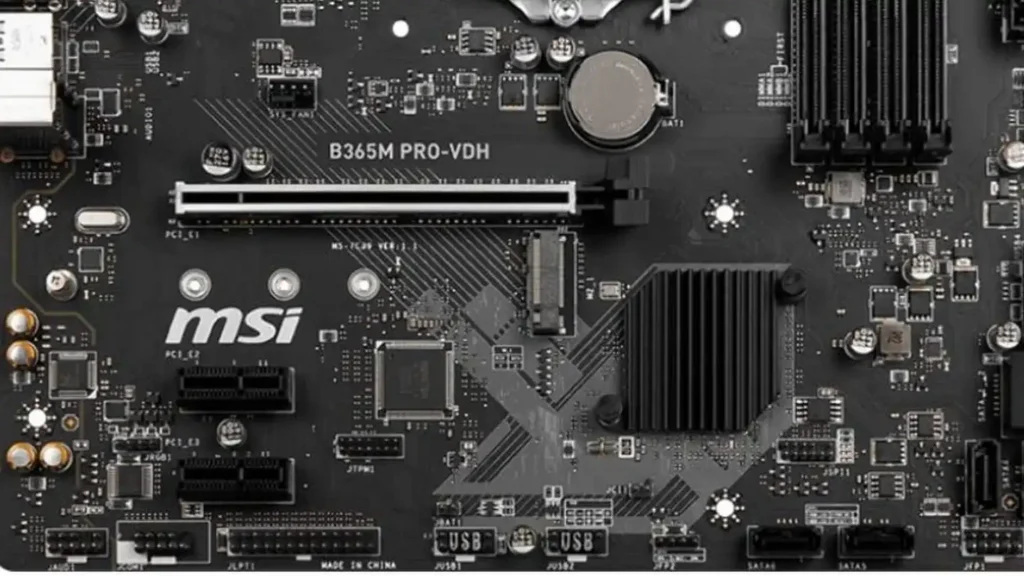

- Definition: The pump fan header on a motherboard is a dedicated connector designed to power and control the pump of a liquid cooling system. This header ensures that the pump operates at the correct speed to efficiently circulate coolant through the system, helping to manage the temperature of critical components like the CPU or GPU.
- Purpose: Unlike standard fan headers, which control airflow, the pump fan header is specifically tailored to handle the constant operation of a liquid cooling pump. It often delivers a steady power supply to ensure the pump runs continuously, preventing overheating and maintaining stable temperatures.
How the Pump Fan Header Works:
- Constant Power Supply: The pump fan header typically provides a consistent 12V power supply, ensuring the pump runs at a constant speed. This is crucial because the pump needs to circulate coolant without interruption to maintain optimal cooling performance.
- Control Options: Some motherboards allow for manual or automatic control of the pump speed through BIOS settings or software, depending on the cooling system’s requirements. This flexibility helps in fine-tuning the cooling performance to match the system’s workload.
- Compatibility: It’s essential to connect the pump of your liquid cooling system to the designated pump fan header. Using a standard fan header instead may not provide the necessary power or control, potentially leading to inadequate cooling.
The Importance of the Pump Fan Header in Liquid Cooling:
- Efficient Cooling: The pump fan header is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of a liquid cooling system. By ensuring that the pump operates continuously and at the correct speed, it prevents the coolant from stagnating, which could lead to overheating and potential damage to components.
- System Stability: Properly using the pump fan header contributes to overall system stability. If the pump were to fail or not operate at the correct speed, it could cause the system to overheat, leading to thermal throttling or even hardware failure.
- Noise Control: Some advanced motherboards and cooling systems allow you to adjust the pump speed based on temperature readings, balancing cooling efficiency with noise levels. A slower pump speed can reduce noise, while a faster speed ensures better cooling under heavy loads.
How to Set Up and Configure the Pump Fan Header:
- Connecting the Pump: When setting up your liquid cooling system, connect the pump’s power cable to the designated pump fan header on your motherboard. This header is usually labeled as “PUMP_FAN” or “AIO_PUMP” and is often found near the CPU socket.
- BIOS Settings: Access your motherboard’s BIOS to configure the pump fan settings. Depending on your motherboard, you may have options to set the pump to run at full speed or to adjust its speed based on temperature. For most systems, keeping the pump at a constant speed is recommended for optimal performance.
- Software Control: Some motherboards offer software tools that allow you to monitor and control the pump fan settings directly from your operating system. These tools can provide real-time feedback on the pump’s performance, enabling you to make adjustments as needed.
Also Read: What If Ram Speed Is Higher Than Motherboard – A Complete Overview!
Common Issues and Troubleshooting:
- Pump Not Running: If the pump isn’t running, check that it’s correctly connected to the pump fan header. Ensure that the header is configured to deliver the necessary power in the BIOS.
- Overheating: If your system is overheating, verify that the pump is running at the correct speed. You may need to adjust the BIOS settings or check for any obstructions in the cooling loop that could be hindering the coolant flow.
- Noise Levels: If the pump is making excessive noise, consider adjusting the pump speed through BIOS or software settings. However, be cautious, as reducing the pump speed too much could impact cooling performance.
FAQ’s
1. What is a pump fan header on a motherboard?
The pump fan header is a dedicated connector that powers and controls the pump in a liquid cooling system.
2. Why is the pump fan header important?
It ensures the pump runs at a constant speed, providing continuous coolant circulation to prevent overheating.
3. Can I connect a pump to a standard fan header?
It’s not recommended, as standard fan headers may not provide the necessary power and control for the pump.
4. How do I configure the pump fan header in BIOS?
Access the BIOS settings, where you can set the pump to run at full speed or adjust its speed based on system temperature.
5. What should I do if my pump isn’t running?
Check the connection to the pump fan header and ensure it’s properly configured in the BIOS.
6. Will using the pump fan header reduce noise?
Some motherboards allow pump speed adjustments, balancing cooling efficiency with noise levels.
7. What happens if the pump fan header isn’t used correctly?
Incorrect usage can lead to system instability, overheating, and potential hardware damage.
8. Is it necessary to monitor the pump fan performance?
Yes, monitoring ensures the pump operates effectively, maintaining optimal cooling and system stability.
Conclusion
The pump fan header on your motherboard plays a vital role in the functionality and efficiency of liquid cooling systems. By providing a consistent power supply and enabling control over pump speed, this header ensures that your system remains cool and stable, even under heavy workloads. Properly setting up and configuring the pump fan header is key to maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of your PC’s components.

Blog
Best Practices For Long-Lasting Asphalt Pavements: What Property Owners Should Know
Why Asphalt Durability Matters For Property Owners
The durability of your asphalt pavement impacts everything from curb appeal to long-term maintenance costs. Whether you manage a commercial parking lot, residential driveway, or community pathway, investing in resilient pavement means fewer disruptions and lower repair costs. This is why many property owners trust experts in asphalt paving La Porte IN to guide them through best practices for installation and upkeep.
Asphalt continues to be a top choice due to its reliable performance and cost-effectiveness. However, even premium-quality asphalt requires proper care to maximize its life span. Research indicates that property owners who take a proactive approach to asphalt maintenance avoid premature replacements and benefit from reduced environmental impact, as maintenance reduces resource consumption and waste generation. For those located in regions with fluctuating weather, such as La Porte, IN, these considerations become even more critical.
Common Causes Of Asphalt Deterioration
Over time, even the best-constructed asphalt surfaces will face wear and tear. Common causes include frequent freeze-thaw cycles, exposure to UV radiation, heavy vehicle traffic, and contaminants like oil or gasoline. Additionally, standing water and debris buildup hasten deterioration, leading to visible issues like cracks, potholes, and fading. These issues can escalate quickly if not addressed, risking aesthetics and safety for those who use the pavement.
Regular and timely interventions, as advised by industry professionals and resources such as the American Society of Civil Engineers, can significantly extend pavement life and delay costly repairs. Adopting modern, climate-resistant asphalt mixes tailored to local conditions helps reduce the risk of structural failures and surface issues, ensuring that your investment remains protected year after year.
Routine Maintenance Strategies That Work
- Sealcoating: This surface treatment acts as a protective barrier, shielding the asphalt from sun, water, and chemicals. Applied every 2–4 years, sealcoating slows the natural aging process and keeps the pavement looking fresh.
- Crack Sealing: Properly addressing cracks prevents water intrusion, which can undermine the sub-base and trigger potholes. Specialized sealants or fillers ensure a watertight seal for cracks of varying sizes.
- Sweeping and Debris Removal:Regularly cleaning the pavementprevents damage caused by trapped moisture and invasive weeds, which accelerate the asphalt binder’s breakdown.
- Regular Inspections: Professional or routine walk-throughs twice a year can reveal early signs of trouble, allowing for minor, affordable fixes before they develop into significant issues.
Design Factors That Influence Asphalt Longevity
Superior asphalt pavement starts with an innovative design. Integral to this is effective drainage—graded surfaces and strategically placed channels or drains ensure water flows away, minimizing the risk of cracks and potholes caused by pooling. The strength and durability of the foundation matter too. Stabilizing and compacting the soils underneath creates a solid base, preventing future settling or deformation.
Material selection is equally important. Especially in climates with dramatic temperature shifts, contractors recommend asphalt mixes with specialized binders or polymers that resist cracking. According to Asphalt Magazine, advances in materials science are enabling longer-lasting pavements that maintain flexibility and integrity, even after years of exposure to harsh weather and high traffic loads.

Addressing Potholes And Surface Damage Quickly
Unattended potholes quickly worsen and pose hazards to both vehicles and pedestrians. Temporary repairs using cold patch materials can prevent accidents in the short term, but a comprehensive fix requires the removal and replacement of compromised pavement with hot mix asphalt. For heavily trafficked commercial properties, resurfacing large worn sections may offer better long-term value than repeated patching. Quick response is crucial to prevent minor flaws from turning into significant liabilities.
The Environmental Side Of Asphalt Maintenance
Sustainability in pavement management is not only environmentally responsible but can also save costs. Many contractors recycle old asphalt, reducing landfill use and raw material expenses. Using eco-friendly sealants and low-VOC surface treatments aligns pavement care with local environmental regulations while minimizing harmful emissions. For property owners looking to make a positive ecological impact, requesting recycled content and green products from contractors is an easy first step. Learn more from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Professional Services Vs. DIY Solutions
While property staff can handle some maintenance tasks, like sweeping or inspecting, larger tasks often require professional experience. Deep structural cracks, major water drainage concerns, or full surface replacements benefit from expert attention to guarantee proper materials, techniques, and compliance with local building codes. Partnering with experienced teams ensures superior workmanship and enlists their insights for ongoing pavement care strategies.
Long-Term Savings From Preventive Care
Reactive repairs quickly add up in both cost and disruption. Studies affirm that implementing a preventive maintenance plan can cut asphalt lifecycle expenses by up to 30%, mainly by avoiding major repairs and extending pavement usability. Beyond financial benefits, regularly maintained asphalt boosts property value, strengthens first impressions for tenants or customers, and enhances overall safety.
Blog
Zuschneidfelle – Your Complete Guide to Cut Fur Materials

In the world of textiles and crafts, fur has always held a special place. From its warmth and softness to its elegance, fur materials have been used for centuries in clothing, accessories, and interior design.
One of the terms you’ll often come across in German marketplaces and craft shops is “zuschneidfelle”, which directly translates to “cut fur pieces.” These are pre-cut sections of natural or artificial fur designed for easy use in DIY projects, fashion, upholstery, and other creative applications.
This guide will help you understand what zuschneidfelle are, their uses, benefits, and how you can choose the best ones for your needs.
What Are Zuschneidfelle?
Definition and Origin
The word “zuschneidfelle” combines two German words:
- “zuschneiden” meaning to cut
- “Felle” meaning furs or skins
Together, it refers to pre-cut fur pieces made from either real animal hides or synthetic fur.
Why They’re Popular
Instead of purchasing a full hide, many people prefer zuschneidfelle because they’re:
- Affordable
- Easier to handle
- Available in manageable sizes for crafting and sewing
Types of Zuschneidfelle
Natural Fur Pieces
These are made from real animal skins, often sourced as by-products of the leather industry. Common types include:
- Sheepskin
- Goatskin
- Cowhide
- Rabbit fur
Each type has its own texture, durability, and warmth.
Artificial (Faux) Fur Pieces
Made from synthetic fibers, faux zuschneidfelle offer:
- A cruelty-free option
- Wide variety of colors and patterns
- Easy maintenance
Common Uses of Zuschneidfelle
1. Fashion and Accessories
Designers often use zuschneidfelle for:
- Coats and jackets
- Fur collars and trims
- Gloves and hats
- Handbags and clutches
2. Interior Decoration
Cut fur pieces are also popular in home design, such as:
- Cushion covers
- Throws and blankets
- Chair upholstery
- Rugs and mats
3. Crafting and DIY Projects
Hobbyists love zuschneidfelle for creative projects like:
- Doll clothing
- Costumes
- Pet accessories
- Art installations
Benefits of Using Zuschneidfelle
Convenience
Pre-cut sizes save time, making them easier to work with than whole hides.
Cost-Effectiveness
Buying smaller pieces reduces costs compared to purchasing a full skin.
Versatility
They can be used for both professional design and small DIY projects.
Eco-Friendly Options
Many zuschneidfelle are by-products, ensuring sustainable use of resources.
How to Choose the Right Zuschneidfelle
Check the Material
Decide whether you want natural fur for authenticity or faux fur for ethical and practical reasons.
Consider the Size
Measure your project needs and choose a piece that matches.
Look at Color and Texture
Select a fur type that complements your design vision—smooth, fluffy, patterned, or plain.
Quality Matters
Ensure the fur is well-processed, durable, and free from defects.
Caring for Zuschneidfelle
Cleaning Tips
- Shake and brush regularly to remove dust.
- For natural fur, avoid soaking in water.
- For faux fur, gentle machine washing may be possible (check labels).
Storage Advice
- Store in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid direct sunlight to prevent fading.
- Use breathable fabric bags instead of plastic.
Where to Buy Zuschneidfelle
Online Stores
Many craft and fabric retailers sell zuschneidfelle online with different sizes, textures, and colors.
Local Craft Shops
You can often find small batches of fur pieces in fabric stores or leather supply shops.
Specialized Fur Dealers
For high-quality natural fur, specialized suppliers may be the best option.
Sustainability and Ethics
Natural Fur Debate
While natural zuschneidfelle are durable and authentic, there are ethical concerns around animal use.
Faux Fur Advantage
Faux options provide cruelty-free alternatives, though they raise questions about synthetic waste.
Eco-Friendly Practices
Some manufacturers now focus on recycled fur or upcycled leather industry by-products, balancing quality with responsibility.
Tips for DIY Projects with Zuschneidfelle
Use the Right Tools
Sharp scissors, rotary cutters, and strong needles are essential.
Plan Your Design
Sketch and measure before cutting to avoid wasting material.
Combine with Other Fabrics
Mixing fur with leather, denim, or cotton creates stylish contrasts.
Start Small
If you’re new to working with fur, begin with a simple project like a pillow cover or keychain.
Customer Experiences with Zuschneidfelle
Positive Reviews
- Affordable for small projects
- Easy to handle compared to full hides
- Great variety of textures and colors
Common Challenges
- Natural fur requires extra care
- Faux fur can shed if poorly made
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What does zuschneidfelle mean?
It means “cut fur pieces” in German.
Is zuschneidfelle real fur?
It can be either natural or synthetic, depending on the source.
Can beginners work with zuschneidfelle?
Yes, they’re easier to handle than full hides, making them beginner-friendly.
Are they expensive?
Prices vary, but small pieces are generally affordable compared to full animal skins.
Final Thoughts on Zuschneidfelle
Whether you’re a fashion designer, home decorator, or hobby crafter, zuschneidfelle offer a practical and versatile way to work with fur. They save time, money, and effort while opening up endless creative possibilities.
From authentic natural hides to eco-friendly faux options, there’s a zuschneidfelle piece for every project. By learning how to choose, care for, and use them effectively, you can elevate your designs while staying mindful of sustainability.
Blog
Your Go-To Air Fryer Cookbook: Recipes for Every Craving

Air fryers have become one of the most popular kitchen gadgets in recent years, and for good reason. They make it easy to enjoy your favorite fried foods without the extra oil, mess, and calories. Whether you’re looking for healthy snacks, quick breakfasts, or family-friendly dinners, an air fryer can do it all. In this roundup, we’ve gathered some of the best high-quality air fryer recipes that you’ll want to make again and again.
From crispy vegetables to perfectly cooked proteins, these dishes prove that air fryers aren’t just a trend—they’re here to stay.
Why Choose the Air Fryer?
Unlike deep frying, which submerges food in hot oil, an air fryer uses rapid air circulation to crisp up food with little to no oil. This makes it a healthier option while still giving you that satisfying crunch and flavor.
Air fryers are also versatile, allowing you to bake, roast, and even dehydrate foods. Busy home cooks love them because meals can be prepared faster, and cleanup is minimal. If you’re on a specific diet, the air fryer can help you whip up meals that are both convenient and delicious.
Breakfasts to Start the Day Right
1. Air Fryer Breakfast Potatoes
Who doesn’t love crispy, golden breakfast potatoes? With an air fryer, you can achieve that perfect balance of crunch and softness without excess oil. Toss diced potatoes with olive oil, paprika, garlic powder, and onion powder, then air fry until golden brown. Pair with eggs or avocado toast for a hearty start to your day.
2. Fluffy Air Fryer Pancakes
Yes, you can even make pancakes in an air fryer! By pouring pancake batter into silicone molds or ramekins, you get fluffy, cake-like pancakes that are fun to serve. Top with fresh fruit, syrup, or nut butter for a wholesome breakfast.
3. Air Fryer Eggs
If you’ve never tried making air fryer eggs, you’re missing out on a quick, protein-packed breakfast. You can cook hard-boiled eggs in the shell, bake mini frittatas in ramekins, or make scrambled eggs in minutes. It’s a versatile method that takes the guesswork out of stovetop cooking.
Snack Attack: Crispy and Healthy Treats
4. Air Fryer Kale Chips
Looking for a healthy snack? Kale chips are light, crunchy, and loaded with nutrients. Simply season kale leaves with olive oil and a sprinkle of sea salt, then air fry until crispy. They’re a guilt-free substitute for potato chips.
5. Buffalo Cauliflower Bites
Perfect for game day or movie night, these cauliflower bites pack bold flavor without the calories of fried wings. Toss florets in buffalo sauce, coat lightly with almond flour, and air fry until crispy. Serve with ranch or blue cheese dip for the ultimate snack.
6. Air Fryer Mozzarella Sticks
Indulge in gooey, cheesy goodness with homemade mozzarella sticks. Freeze breaded cheese sticks before popping them in the air fryer. The result? A crispy outer layer with a melted center—perfect for dipping into marinara sauce.
Lunchtime Favorites
7. Crispy Chicken Tenders
Chicken tenders are a family classic, and the air fryer makes them even better. Coat strips of chicken in seasoned breadcrumbs or panko, then air fry until golden brown. These are great for kids’ lunches or quick weeknight meals.
8. Air Fryer Fish Tacos
For a lighter twist, try air fryer fish tacos. Use a white fish like cod or tilapia, season with chili powder and lime, and air fry until flaky. Serve with shredded cabbage, avocado, and a drizzle of crema on corn tortillas.
9. Stuffed Bell Peppers
Air fryers are excellent for cooking stuffed vegetables. Bell peppers stuffed with quinoa, beans, veggies, and cheese cook evenly and develop a slightly charred flavor that enhances every bite.
Dinner Made Easy
10. Juicy Air Fryer Salmon
If you’re looking for a healthy and quick dinner option, salmon is a top choice. The air fryer locks in moisture while crisping up the outside. Season with lemon, garlic, and dill, and serve with roasted veggies or rice.
11. Air Fryer Meatballs
These meatballs are tender, flavorful, and easy to prepare. Combine ground beef or turkey with breadcrumbs, Parmesan, and Italian herbs, then air fry until golden. They’re perfect for spaghetti night or served as appetizers with dipping sauce.
12. Crispy Tofu Stir-Fry
For a vegetarian-friendly dinner, crispy tofu works beautifully in the air fryer. Toss cubes of tofu with soy sauce, sesame oil, and cornstarch, then air fry until golden. Add them to a stir-fry with your favorite vegetables and sauce.
Sweet Treats to End the Day
13. Air Fryer Donuts
Skip the deep fryer and make light, fluffy donuts in your air fryer. Use biscuit dough or homemade dough, cook until golden, and then roll in cinnamon sugar. They’re a fun dessert that feels indulgent but is lighter than the traditional version.
14. Baked Apples
Core apples and stuff them with oats, cinnamon, nuts, and honey, then air fry until tender. This dessert is both wholesome and comforting, perfect for cool evenings.
15. Chocolate Lava Cakes
Yes, you can even make decadent lava cakes in your air fryer. With just a few ingredients, you’ll get a gooey chocolate center surrounded by a fluffy cake exterior—ideal for date night or when you’re craving something sweet.
Final Thoughts
Air fryers have transformed the way we cook at home, making it easier than ever to enjoy crispy, delicious meals with fewer calories and less effort. From quick breakfasts to indulgent desserts, the possibilities are endless. Whether you’re looking for healthy snacks, or creative family dinners, this recipe roundup has something for everyone.
If you haven’t yet explored the full potential of your air fryer, now is the perfect time to start experimenting. These recipes are just the beginning—once you get comfortable, you’ll find yourself air frying almost everything.
So dust off your air fryer, gather your ingredients, and get ready to create meals that are not only quick and healthy but also bursting with flavor. Your taste buds (and your waistline) will thank you.
-

 Tech7 months ago
Tech7 months agoSotwe STW Explained How a Radical Platform is Redefining Online Expression
-

 Entertainment8 months ago
Entertainment8 months agoHow Do I Turn On the Beatbot?
-

 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoAre B750 Motherboard A Good Choice – A Complete Overview!
-

 Blog1 year ago
Blog1 year agoHow To Find My Motherboard Model And Bios Version – A Detailed Overview!
-

 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoAre Gigabyte Motherboards Good – A Comprehensive Review!
-
Motherboard Guide4 months ago
The Ultimate Croatia Travel Guide for First-Timers: Everything You Need to Know Before You Go
-

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoHer Love Is A Kind Of Charity Password – The Hidden Meaning Behind the Phrase!
-
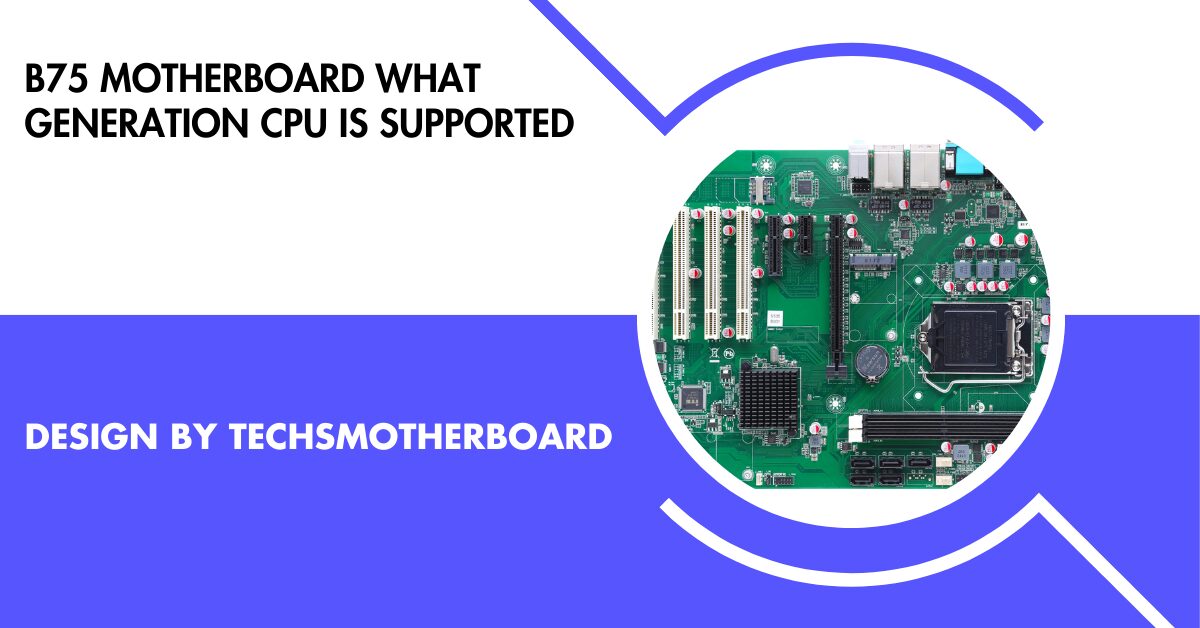
 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoB75 Motherboard What Generation Cpu Is Supported – B75 Motherboard Cpu Support!