Specialized Motherboard
Are All Ssd Compatible With All Motherboards – A Complete Overview!

Not all SSDs are compatible with all motherboards; compatibility depends on the SSD type, available slots, and chipset capabilities.
This guide will help you understand how to ensure compatibility between your SSD and motherboard.
Types of SSDs:
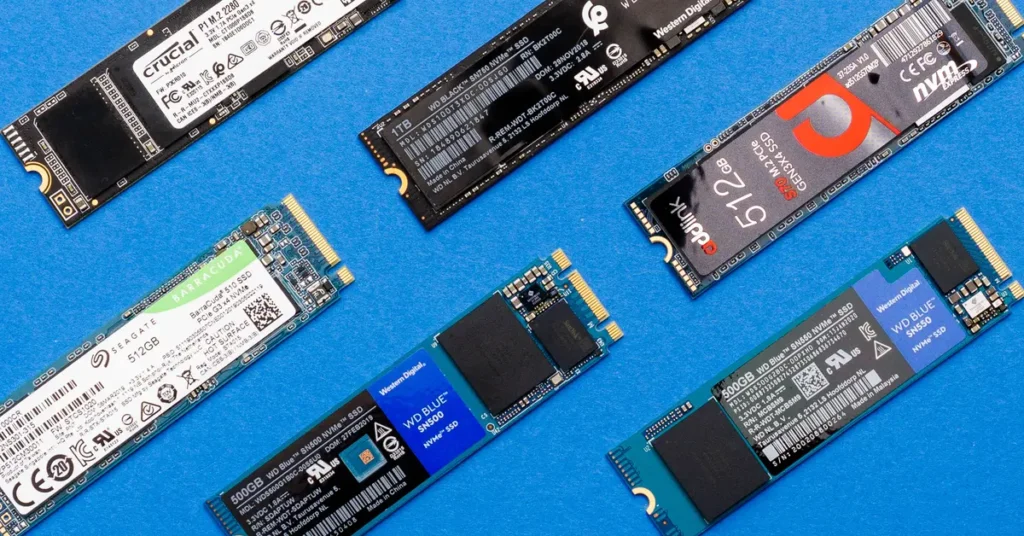

There are several types of SSDs available on the market, each with unique features, speeds, and form factors. The three most common SSD types are:
SATA SSDs:
SATA (Serial ATA) SSDs are one of the most popular types of SSDs due to their wide compatibility. These SSDs use the same SATA interface that mechanical hard drives use, making them an excellent choice for users upgrading from HDDs (Hard Disk Drives).
- Compatibility: Most modern motherboards support SATA SSDs through dedicated SATA ports. Even older motherboards can typically handle SATA SSDs, making them an excellent option for older PCs or budget builds.
- Speed: While significantly faster than HDDs, SATA SSDs are slower than other types of SSDs, such as NVMe SSDs. SATA SSDs generally offer data transfer speeds of up to 550MB/s.
- Form Factor: SATA SSDs are usually available in a 2.5-inch form factor, the same as laptop hard drives. Some come in an M.2 form factor but still operate over the slower SATA bus.
NVMe (M.2) SSDs:
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs are the fastest SSDs on the market, using the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface instead of the SATA interface. They typically come in the M.2 form factor, a small, compact size ideal for high-performance setups.
- Compatibility: NVMe SSDs require an M.2 slot that supports PCIe lanes. Not all M.2 slots support NVMe, so it’s crucial to verify that your motherboard’s M.2 slot is compatible with PCIe NVMe SSDs. Some older or budget motherboards may lack this slot entirely.
- Speed: NVMe SSDs offer incredibly high speeds, ranging from 2,000MB/s to over 7,000MB/s, depending on whether they use PCIe 3.0, 4.0, or 5.0 lanes. These speeds make NVMe SSDs ideal for gaming, video editing, and other demanding tasks.
- Form Factor: NVMe SSDs commonly use the M.2 form factor, which is much smaller than traditional 2.5-inch SATA SSDs. M.2 NVMe drives are ideal for systems where space is at a premium, such as ultrabooks and mini-ITX PCs.
PCIe SSDs:
PCIe SSDs are another high-performance option, plugging directly into the motherboard’s PCIe slots, much like a graphics card. These SSDs are often used in workstations or servers where maximum performance is required.
- Compatibility: To use a PCIe SSD, your motherboard must have available PCIe slots. These SSDs are typically larger and less common than M.2 NVMe SSDs, but they offer the same blazing-fast speeds.
- Speed: PCIe SSDs offer performance on par with NVMe drives, as they utilize the same PCIe lanes. However, the availability of PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 5.0 motherboards can unlock even higher speeds.
- Form Factor: Unlike M.2 SSDs, PCIe SSDs are larger, often using a full-size PCIe expansion slot, making them less suitable for compact builds but ideal for high-performance desktops.
Also Read: How To Update Motherboard Bios – A Complete Guide!
Key Motherboard Compatibility Factors:
Now that you’re familiar with the different types of SSDs, let’s dive into the essential factors that determine whether an SSD is compatible with your motherboard.
Motherboard SSD Slots:
The most critical factor is ensuring that your motherboard has the right type of slot for the SSD you’re planning to install.
- SATA Ports: If you’re installing a SATA SSD, you need an available SATA port on your motherboard. Most motherboards offer multiple SATA ports, but compact or older boards may have fewer.
- M.2 Slots: For NVMe SSDs, your motherboard must have an available M.2 slot that supports PCIe NVMe SSDs. Some motherboards have multiple M.2 slots, but not all M.2 slots support NVMe; some may only work with SATA-based M.2 SSDs.
- PCIe Slots: For PCIe SSDs, you’ll need an available PCIe expansion slot. Be mindful that installing a PCIe SSD may limit the number of PCIe lanes available for other components, such as your graphics card.
Chipset and PCIe Version:
Motherboard chipsets and PCIe versions also play a role in compatibility.
- Chipset Compatibility: Newer chipsets, like Intel’s Z590 or AMD’s X570, support the latest PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 5.0 standards, allowing for faster data transfer speeds with NVMe SSDs. Older motherboards may only support PCIe 3.0, limiting your SSD’s speed potential.
- PCIe Version: If your motherboard supports PCIe 4.0 or PCIe 5.0, you can take full advantage of the higher speeds offered by the latest NVMe SSDs. Motherboards with PCIe 3.0 slots will limit your SSD to PCIe 3.0 speeds, even if your drive supports faster speeds.
BIOS Updates:
BIOS updates can often improve compatibility with newer SSDs, particularly NVMe drives. If your motherboard does not recognize a newly installed SSD, checking for a BIOS update is a good first step. Updating the BIOS can unlock support for newer drives, fix bugs, and improve system stability.
How to Ensure SSD Compatibility Before Purchase:
Consult Your Motherboard Manual:
Your motherboard’s manual will provide detailed information about the available ports and supported SSDs. It’s the best resource for checking compatibility before purchasing an SSD.
Check Manufacturer’s Website:
Most motherboard manufacturers offer compatibility lists on their websites. By entering your motherboard model, you can access a list of supported SSD types, speeds, and form factors.
Use Online Compatibility Tools:
There are several online tools and compatibility databases that allow you to input your motherboard model and receive a list of compatible SSDs. These tools can help take the guesswork out of choosing the right drive for your system.
Common Compatibility Issues and Solutions:
Form Factor Mismatch:
One common issue is purchasing an SSD that does not physically fit in your motherboard. For example, buying an M.2 SSD when your motherboard only has SATA ports, or a PCIe SSD for a system with limited expansion slots. Always check your motherboard’s available slots and form factor support before buying.
Incorrect M.2 Slot:
Some M.2 slots only support SATA SSDs, while others support NVMe drives. It’s crucial to confirm that your motherboard’s M.2 slot supports the specific type of SSD you’re installing. M.2 slots may look the same but offer different types of connectivity.
Insufficient PCIe Lanes:
Installing an NVMe or PCIe SSD requires available PCIe lanes. If your graphics card or other components are using too many lanes, your SSD may not perform at its full potential, or you may not be able to install it at all.
Outdated BIOS:
An outdated BIOS can prevent your motherboard from recognizing newer SSDs. Check for BIOS updates if you encounter issues with your SSD, as a simple update could resolve the problem.
FAQ’s
1. Can I use any SSD with my motherboard?
No, you need to check if your motherboard supports the specific type of SSD, such as SATA, NVMe, or PCIe.
2. What is the difference between SATA and NVMe SSDs?
SATA SSDs use the older SATA interface and offer slower speeds, while NVMe SSDs use the PCIe interface, providing much faster data transfer rates.
3. Do all motherboards have M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs?
No, not all motherboards have M.2 slots, and some that do may only support SATA M.2 drives, not NVMe.
4. What happens if my SSD is not recognized by the motherboard?
This could be due to an outdated BIOS. Updating the BIOS may help the motherboard recognize the SSD.
5. Can a PCIe SSD work in any motherboard?
A PCIe SSD requires an available PCIe slot, and the performance may be limited if the motherboard only supports an older PCIe version like PCIe 3.0.
Conclusion
In summary, not all SSDs are compatible with all motherboards. Compatibility depends on several factors, including the SSD type (SATA, NVMe, PCIe), the form factor, the motherboard’s available slots, and the chipset’s capabilities. By consulting your motherboard manual, checking compatibility tools, and ensuring your BIOS is up to date, you can confidently choose the right SSD for your system. A properly selected and compatible SSD will enhance your computer’s performance, delivering faster load times, improved responsiveness, and a more efficient computing experience.
Specialized Motherboard
How To Download Windows On My Motherboard – A Step-By-Step Guide!

Visit the Microsoft website, download the Media Creation Tool, create a bootable USB, and boot from it to install Windows on your motherboard.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps you need to take to download Windows and install it on your motherboard with ease.
What You Need Before Installing Windows:
Before you start the installation process, it’s important to make sure you have all the necessary tools and preparations in place. Here’s a checklist:
- A Valid Windows License Key: You will need a valid Windows product key to activate the operating system.
- A USB Flash Drive: At least 8GB in size is recommended to create a bootable installation drive.
- A Windows PC or Laptop: You’ll need another computer to download the Windows ISO file and prepare the installation drive.
- Internet Connection: A stable internet connection is necessary for downloading the installation files and any updates during installation.
- Motherboard with a Compatible Processor: Ensure your motherboard is compatible with Windows. Most modern motherboards are, but it’s always good to check the specifications.
Why Do You Need a Motherboard for Windows Installation?
The motherboard is the central hub of your computer. It’s where all the critical components, such as the processor, memory, and storage devices, are connected. Installing Windows on your motherboard means setting up the operating system to work seamlessly with all the hardware components installed.
In the next sections, we’ll show you the steps to follow for downloading and installing Windows on your motherboard.
Download the Windows ISO File:
The first step in installing Windows on your motherboard is downloading the Windows ISO file. The ISO file is a digital copy of the Windows operating system that you’ll later use to create a bootable USB drive.
How to Download Windows from Microsoft’s Official Website:
- Visit the Microsoft Website: Go to the official Microsoft website by typing “Windows download” in your search engine or directly visiting Microsoft’s Windows Download Page.
- Select the Windows Version: Choose the version of Windows you want to install. Windows 10 and Windows 11 are the most common choices, so make sure you select the right one for your needs.
- Download the Media Creation Tool: Click on the “Download tool now” button for the Media Creation Tool. This is a small program that helps you create the installation USB.
- Run the Tool: After downloading the tool, run it on your computer. You’ll be asked to accept the terms and conditions.
- Select “Create Installation Media”: Choose the option “Create installation media for another PC” and click Next. You’ll be asked to choose the language, edition, and architecture (32-bit or 64-bit) for your Windows version. Most modern systems use 64-bit, so ensure that you select it.
- Choose USB Flash Drive: Next, select the USB flash drive option. Ensure the drive is empty, as all data will be erased during the process.
- Wait for the Download: The tool will start downloading Windows and transfer the installation files to the USB drive. This might take some time depending on your internet speed.
Also read: Can Your Motherboard Use Any Ssd – A Complete Guide!
Prepare the USB Drive for Installation:
Once the download is complete, your USB flash drive will be set up as a bootable device. This means you can use it to start the Windows installation on your motherboard. Now, let’s prepare your computer to boot from the USB drive.
How to Set Your Computer to Boot from USB:
- Insert the USB Flash Drive: Insert the USB drive into one of the USB ports on your computer.
- Access BIOS/UEFI Settings: To make the computer boot from the USB drive, you need to access the BIOS or UEFI settings. Restart your computer and press the designated key (usually F2, DEL, or ESC) during the boot process. This key can vary depending on your motherboard, so refer to the motherboard manual if you’re unsure.
- Change Boot Order: Once you’re in the BIOS/UEFI settings, navigate to the “Boot” or “Boot Order” section. Use the arrow keys to select the USB drive as the first boot device. Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI.
- Restart the Computer: After exiting the BIOS, your computer should restart. It will now boot from the USB drive and begin the Windows installation process.
Install Windows on Your Motherboard:
After booting from the USB drive, you’ll see the Windows installation screen. Now, you can start the installation process.
How to Install Windows:
- Select Language and Preferences: The installation wizard will ask you to choose your language, time zone, and keyboard layout. Select the appropriate options and click Next.
- Start the Installation: Click Install Now to begin the installation process. You’ll be prompted to enter the product key. If you have one, enter it; otherwise, you can skip this step and enter it later.
- Choose Installation Type: You’ll be asked whether you want to upgrade an existing version of Windows or do a clean installation. Select Custom: Install Windows Only if you want a fresh installation.
- Select the Hard Drive: The next step is to select the drive where Windows will be installed. If your computer has multiple drives, choose the one you want to use for the installation. If necessary, format the drive by selecting Drive Options and choosing Format.
- Wait for the Installation: Windows will start installing on your motherboard. This process can take some time, depending on the speed of your computer and the drive. Your computer will restart multiple times during the installation.
- Set Up Windows: After the installation is complete, your computer will reboot into Windows. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup, including creating a user account and setting up your preferences.
Install Drivers for Your Motherboard:

Once Windows is installed, it’s time to make sure everything works properly by installing the necessary drivers. Drivers are software that allows your hardware to communicate with your operating system.
How to Install Drivers:
- Visit the Motherboard Manufacturer’s Website: Go to the website of your motherboard’s manufacturer (e.g., ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, etc.).
- Find the Drivers Section: Search for the “Support” or “Downloads” section, and select your motherboard model.
- Download the Drivers: Download the drivers for your motherboard’s chipset, network, audio, and other components. These drivers will help ensure your hardware works smoothly with Windows.
- Install the Drivers: Once the drivers are downloaded, open the installation files and follow the on-screen instructions to install them.
- Restart the Computer: After installing the drivers, restart your computer to ensure all changes take effect.
Activate Windows:
To fully enjoy all the features of Windows, you’ll need to activate it using a valid product key. If you didn’t enter the product key during installation, you can do it after the setup is complete.
How to Activate Windows:
- Open Settings: Click on the Start menu, then go to Settings (the gear icon).
- Go to Update & Security: In the settings window, click on Update & Security, then select Activation from the left menu.
- Enter the Product Key: If you have a valid product key, click on Change Product Key and enter the key.
- Activate Windows: After entering the product key, click Next and follow the prompts to activate Windows.
How do I download a window operating system?
To download a Windows operating system, visit the official Microsoft website and select the version you want, such as Windows 10 or Windows 11. Download the Media Creation Tool, which will help you download the OS and create installation media. After running the tool, choose to either upgrade your system or create a bootable USB drive. Insert the USB into your target computer, restart it, and boot from the USB. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation, ensuring you have a valid license.
FAQs
1. What do I need before installing Windows?
You need a valid Windows license key, a USB flash drive (at least 8GB), a second PC to download the Windows ISO, a stable internet connection, and a compatible motherboard.
2. How do I prepare the USB drive for installation?
After downloading the Media Creation Tool from Microsoft’s website, use it to transfer Windows installation files to the USB drive, making it bootable.
3. How do I make my computer boot from the USB?
Access your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings during startup, change the boot order to prioritize the USB drive, save the changes, and restart the computer.
4. What should I do after installing Windows?
Install necessary drivers from the motherboard’s manufacturer website, restart your computer, and then activate Windows using your product key.
5. Can I skip entering a product key during installation?
Yes, you can skip entering the product key during installation and enter it later through the Windows settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, downloading and installing Windows on your motherboard is a straightforward process that involves creating a bootable USB drive using the Media Creation Tool. Once you’ve set up the USB drive and booted from it, the installation of Windows is simple and can be customized to your preferences. Don’t forget to install the necessary drivers and activate your Windows for full functionality.
Related post
Specialized Motherboard
Can Your Motherboard Use Any Ssd – A Complete Guide!

Not all SSDs are compatible with every motherboard. You must check if your motherboard supports the specific SSD interface (SATA, NVMe, M.2) and required slots.
This article will help you understand the compatibility between motherboards and SSDs and guide you in choosing the right one.
What is an SSD?

Before diving into compatibility, let’s first understand what an SSD is. An SSD (Solid-State Drive) is a type of storage device that uses flash memory to store data. Unlike traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), which use spinning disks to read and write data, SSDs have no moving parts. This makes them faster, more durable, and energy-efficient.
SSDs come in various forms, including SATA SSDs, NVMe SSDs, and M.2 SSDs, each with different interfaces and speed capabilities. While all these types offer faster performance than HDDs, their compatibility with your motherboard depends on several factors.
Types of SSDs and Their Interfaces:
SATA SSDs:
SATA SSDs are the most common type and use the same interface as traditional hard drives (HDDs), making them easy to install and widely compatible with most motherboards. They offer solid performance improvements over HDDs but are slower compared to other SSD types like NVMe. SATA SSDs are ideal for users looking for a cost-effective upgrade from an HDD without requiring a specialized motherboard or high-speed storage needs, offering a balanced option for general computing.
NVMe SSDs:
NVMe SSDs deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs. They utilize the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, which allows for much higher bandwidth. Designed for high-performance tasks like gaming, video editing, or data-heavy applications, NVMe SSDs can provide a substantial speed boost. However, they require specific motherboard slots with PCIe lanes, meaning that not all systems can support them. Users need to ensure their motherboard has the appropriate slot for NVMe.
M.2 SSDs:
M.2 is a physical form factor for SSDs, and both SATA and NVMe SSDs are available in this format. The M.2 slot on the motherboard can support either SATA or NVMe SSDs, depending on the motherboard’s capabilities. M.2 drives are more compact than traditional 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, often providing faster performance, especially with NVMe. However, not all motherboards have M.2 slots, particularly older models, so it’s crucial to check compatibility before choosing an M.2 SSD.
Also read: Can You Split Motherboard RGB Header – Simple Guide!
How to Check If Your Motherboard Supports SSDs:
Check the Interface and Slot Type:
To ensure compatibility with your SSD, start by checking whether your motherboard supports the SSD interface. For a SATA SSD, your motherboard should have SATA ports. If you’re using an NVMe SSD, your motherboard must have an M.2 slot that supports PCIe. This step is crucial because the interface dictates the data transfer speed and type of connection your system will utilize. Always verify the correct slots are available before purchasing an SSD.
Verify M.2 Slot Compatibility:
M.2 slots can support either SATA or NVMe SSDs, but not all M.2 slots are the same. Some older motherboards only support SATA M.2 SSDs, while others may support NVMe SSDs. To find out what type your motherboard supports, consult the motherboard’s manual or check online specifications. Understanding the capabilities of your M.2 slots ensures that you select the right SSD type, whether you’re looking for high performance or simply more storage.
PCIe Lanes and NVMe Support:
For NVMe SSDs, it’s important to check if your motherboard has enough PCIe lanes to support faster data transfer speeds. Some older motherboards only support PCIe 2.0, which is slower than newer PCIe 3.0 or 4.0 standards. Verify that your motherboard has PCIe slots that can fully support the speed of the NVMe SSD you’re considering. Ensuring PCIe compatibility is essential to unlocking the full potential of an NVMe SSD, especially for high-performance tasks.
Firmware and BIOS Updates:
Even if your motherboard has the correct slots for an SSD, a firmware or BIOS update may be necessary for full compatibility. Some older BIOS versions may not support newer SSD technologies like NVMe. Before installing your SSD, check for updates to your motherboard’s BIOS to ensure that the system can properly recognize and utilize the new storage device. Keeping your BIOS up to date ensures optimal performance and compatibility with modern SSDs.
Motherboard and SSD Compatibility: Key Considerations
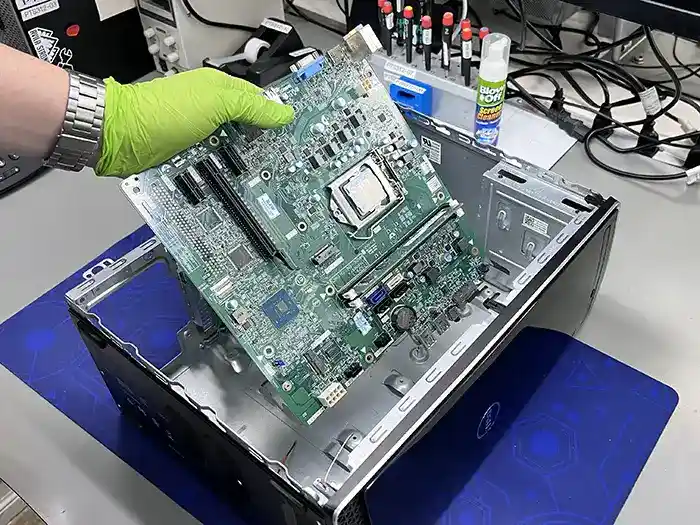

SSD Storage Capacity:
While most modern motherboards support large SSD storage capacities, it’s important to confirm that your motherboard can handle the size of the SSD you plan to install. For instance, NVMe SSDs with large storage capacities require specific motherboard support. Ensure that your motherboard has the necessary interface and slots to support the SSD size, particularly for high-capacity drives. Checking your motherboard’s specifications will prevent issues like inadequate storage support and ensure compatibility with your desired SSD.
Form Factor and Size:
The physical size and form factor of an SSD are crucial when selecting the right one for your motherboard. A standard 2.5-inch SATA SSD fits most motherboards, while NVMe SSDs come in different M.2 form factors, with 2280 being the most common (22mm wide, 80mm long). However, some motherboards support alternative M.2 sizes, such as 2230 or 22110. Verify the M.2 slot on your motherboard to ensure that the SSD’s form factor is compatible before purchasing.
Cooling Requirements:
High-performance NVMe SSDs tend to generate more heat than SATA SSDs, especially during gaming or intensive applications. To ensure proper performance and longevity, your motherboard should ideally have cooling options for the SSD. Many modern motherboards include heatsinks for M.2 slots, but older models may lack this feature. If your motherboard doesn’t have a built-in heatsink, consider purchasing a third-party heatsink to manage temperatures and prevent thermal throttling, ensuring your SSD runs optimally.
Also read: B75 Motherboard What Generation Cpu Is Supported – B75 Motherboard Cpu Support!
How to Install an SSD on Your Motherboard:
Once you’ve confirmed that your motherboard supports the SSD you’re considering, the installation process is usually straightforward.
- Install a SATA SSD: To install a SATA SSD, simply connect the drive to one of the SATA ports on your motherboard using a SATA data cable. Then, connect the power cable from your power supply to the SSD. The computer should recognize the SSD once you boot it up, and you can format it using your operating system.
- Install an NVMe SSD: To install an NVMe SSD, find the M.2 slot on your motherboard, which is typically located near the CPU. Slide the SSD into the slot at an angle and secure it with a small screw. Once installed, boot up the system and make sure the SSD is recognized by your operating system.
Best SSDs for Your Motherboard:
Best SATA SSDs:
If your motherboard supports SATA SSDs, these options are great for overall performance and reliability:
- Samsung 860 EVO
- Crucial MX500
- Western Digital Blue 3D NAND
These SATA SSDs offer solid performance for daily tasks, gaming, and content creation, and are widely compatible with most motherboards.
Best NVMe SSDs:
For faster performance, here are some top-rated NVMe SSDs that will deliver high-speed data transfer:
- Samsung 970 EVO Plus (PCIe 3.0)
- Western Digital Black SN850 (PCIe 4.0)
- Corsair MP600 (PCIe 4.0)
These NVMe SSDs are perfect for gaming, video editing, and other demanding applications, but make sure your motherboard supports PCIe 3.0 or 4.0 for optimal performance.
FAQ’s
1. Can I use any SSD with my motherboard?
No, your motherboard must have the appropriate interface and slots (SATA, M.2, PCIe) to support the SSD type you want to use, ensuring proper compatibility.
2. How do I know if my motherboard supports NVMe SSDs?
Check if your motherboard has an M.2 slot supporting PCIe and verify its specifications to confirm it supports NVMe SSDs. This ensures compatibility with faster, high-performance drives.
3. What is the difference between SATA and NVMe SSDs?
SATA SSDs are slower but more universally compatible, while NVMe SSDs provide faster speeds. NVMe requires specific motherboard slots with PCIe lanes to support its faster data transfer.
4. Can I install an SSD without a special slot on my motherboard?
If your motherboard lacks M.2 or PCIe slots, you can still use a SATA SSD if there’s a compatible SATA port available, offering an easier installation without special slots.
5. Is there a size limit for the SSD I can use with my motherboard?
Yes, some older motherboards may have size or capacity limits for SSDs. It’s important to review your motherboard’s specifications before purchasing to ensure compatibility with your desired SSD.
Conclusion
Not all SSDs are compatible with every motherboard. Ensure your motherboard supports the correct interface (SATA, NVMe, M.2) and has the necessary slots. Reviewing your motherboard’s specifications is key when choosing an SSD to guarantee compatibility, performance, and smooth installation for your system upgrade or build, helping to avoid potential issues with fit or speed.
Related post
Specialized Motherboard
Will Your Motherboard Brick If Turned Off When Updating Bios – Bios Update Tips!

Turning off your motherboard during a BIOS update can brick it, as interruptions may corrupt the BIOS, preventing your system from booting.
In this article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about this issue in simple terms.
What Is a BIOS Update?
Understanding BIOS:
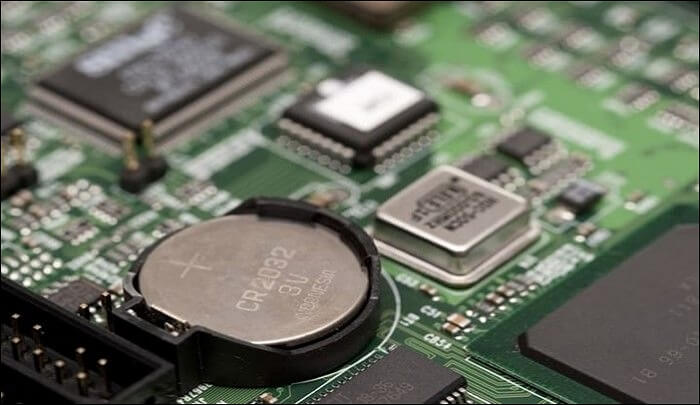

The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is a fundamental program stored on your computer’s motherboard. It manages hardware initialization during startup and facilitates communication between the operating system and various hardware components, such as the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and more. BIOS is critical for the system’s functionality, ensuring everything works correctly. Without it, the computer wouldn’t be able to properly boot up or interact with its internal hardware components.
Why Update the BIOS?
Updating your BIOS can address various issues, such as fixing bugs or errors that affect system performance. It can also add compatibility for newer hardware, like processors or RAM, allowing your computer to support the latest technology. BIOS updates can improve system stability and functionality, enhancing the overall performance of your computer. However, BIOS updates should be performed with caution, as improper updates can cause system malfunctions.
What Happens During a BIOS Update?
The Process of Updating
When you update your BIOS:
- The update rewrites the old BIOS program with a new one.
- The process erases and replaces critical data stored in the BIOS chip.
- It requires uninterrupted power to complete safely.
Why Is Power Important?
Power is crucial during a BIOS update because any interruption, such as a power outage or system shutdown, can prevent the BIOS from being fully installed. An incomplete installation may corrupt the BIOS, leading to a non-functional motherboard. This can result in the system being unable to start or boot properly. To avoid such issues, it’s essential to ensure a stable power supply during the entire update process.
What Does “Bricking” Mean?
“Bricking” refers to a situation where a device, such as a motherboard, becomes completely non-functional, like a brick. A bricked motherboard is unable to boot or operate properly. This can occur if the BIOS update is interrupted, such as during a power failure or shutdown, or if an incorrect version of the BIOS is installed. In both cases, the motherboard may be left unusable, requiring professional repair or replacement to restore functionality.
Will Your Motherboard Brick If Turned Off During a BIOS Update?
Yes, turning off your motherboard or losing power during a BIOS update can lead to bricking. The update process is crucial for properly installing the BIOS, and if interrupted, it can result in an incomplete or corrupted installation. This leaves the system unable to function and may prevent the motherboard from booting. To avoid this, ensure a stable power supply throughout the BIOS update process to prevent potential damage.
How to Avoid Bricking Your Motherboard:
Use a Reliable Power Source:
To prevent interruption during a BIOS update, connect your computer to a reliable power source. Consider using an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to protect against sudden power cuts. This ensures the update process continues smoothly, reducing the risk of a corrupted BIOS. A stable power supply is essential to avoid system failure or motherboard damage, which could occur if power is lost mid-update.
Follow Manufacturer Instructions:
Always follow the manufacturer’s specific instructions when performing a BIOS update. Each motherboard brand has its own recommended procedure. By reading the user manual or checking the official guidelines, you ensure the update is performed correctly. Incorrect steps or skipping essential instructions may result in serious issues like a bricked motherboard. Properly following the manufacturer’s advice ensures the update process goes smoothly and safely.
Also Read: Are B650 Motherboard A Good Choice – A Complete Guide!
Check for Compatibility:
Ensure that the BIOS update file you download matches your motherboard model. Installing the wrong update can lead to critical errors and system failure. Always check the motherboard’s model number and verify the BIOS version from the manufacturer’s website. Compatibility is crucial, and using the incorrect BIOS version can permanently damage the motherboard, making it unresponsive and potentially unrepairable.
Avoid Interruptions:
Do not turn off or restart your computer during the BIOS update process. Interrupting the update can result in an incomplete or corrupted installation, potentially causing a bricked motherboard. Any disruption to the update process may prevent your system from booting properly, leaving it unusable. Let the BIOS update finish without interference to ensure that it installs correctly and that your motherboard continues to function as intended.
What to Do If the BIOS Update Fails?
Try a BIOS Recovery Feature:
Many modern motherboards come with a BIOS recovery feature, such as Dual BIOS or BIOS Flashback. These features allow you to reinstall or repair the BIOS using a backup version stored on the motherboard. To use this, follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, as the process may differ between models. This can help restore your system to a functional state without needing professional assistance.
Contact Customer Support:
If your BIOS update fails, contact the motherboard manufacturer’s support team for guidance. They can offer troubleshooting steps, provide firmware recovery options, or recommend solutions. Manufacturer support is an essential resource for resolving issues related to BIOS failures. They can help ensure the issue is properly diagnosed and provide the correct steps to recover the system, potentially saving you time and preventing further damage.
Seek Professional Help:
If the BIOS recovery tools don’t work, it’s best to seek professional help. A technician or specialized repair service can assess the situation and perform advanced recovery procedures. They may be able to reflash or replace the BIOS chip to restore functionality. Taking your motherboard to a repair service can prevent further damage and ensure the issue is resolved correctly, especially if you’re unable to fix it yourself.
FAQ’S
1. Aan turning off the system during a BIOS update damages the motherboard?
Yes, turning off the system can cause BIOS corruption, making the motherboard unusable, preventing it from booting or functioning properly.
2. How can I avoid bricking my motherboard during a BIOS update?
To avoid bricking, ensure a stable power source, use an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, and avoid interruptions during the update process.
3. What is BIOS “bricking”?
Bricking refers to a situation where the motherboard becomes non-functional due to a failed or incomplete BIOS update, often leaving it unable to boot or operate normally.
4. What should I do if my BIOS update fails?
If a BIOS update fails, use the motherboard’s recovery feature like Dual BIOS or BIOS Flashback, contact customer support, or seek professional repair services to restore functionality.
5. Can I recover my system if the BIOS update is interrupted?
Yes, many modern motherboards have built-in recovery options such as Dual BIOS or BIOS Flashback, which allow you to restore or reinstall the BIOS and recover the system.
Conclusion
Turning off your motherboard during a BIOS update can lead to bricking, making your system unbootable due to corrupted BIOS. To avoid this, ensure a stable power source, use an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. If the update fails, use BIOS recovery features or seek professional help to restore functionality and avoid permanent damage.
-

 Tech7 months ago
Tech7 months agoSotwe STW Explained How a Radical Platform is Redefining Online Expression
-

 Entertainment8 months ago
Entertainment8 months agoHow Do I Turn On the Beatbot?
-

 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoAre B750 Motherboard A Good Choice – A Complete Overview!
-

 Blog1 year ago
Blog1 year agoHow To Find My Motherboard Model And Bios Version – A Detailed Overview!
-

 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoAre Gigabyte Motherboards Good – A Comprehensive Review!
-
Motherboard Guide4 months ago
The Ultimate Croatia Travel Guide for First-Timers: Everything You Need to Know Before You Go
-

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoHer Love Is A Kind Of Charity Password – The Hidden Meaning Behind the Phrase!
-
 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoB75 Motherboard What Generation Cpu Is Supported – B75 Motherboard Cpu Support!